Paper presentation at 11th International Workshop on Spanish Sociolinguistics
Willis, E., Arróniz, S., Galarza, I., and Delgado-Díaz, G. Puerto Ricans may eat their eses, but the taste remains: the perception (or lack) of voiced stops as compensation for deleted coda /s/ by Puerto Rican and Mexican listeners. 11th International Workshop on Spanish Sociolinguistics. The State University of New York, Buffalo. April 2024.
Abstract
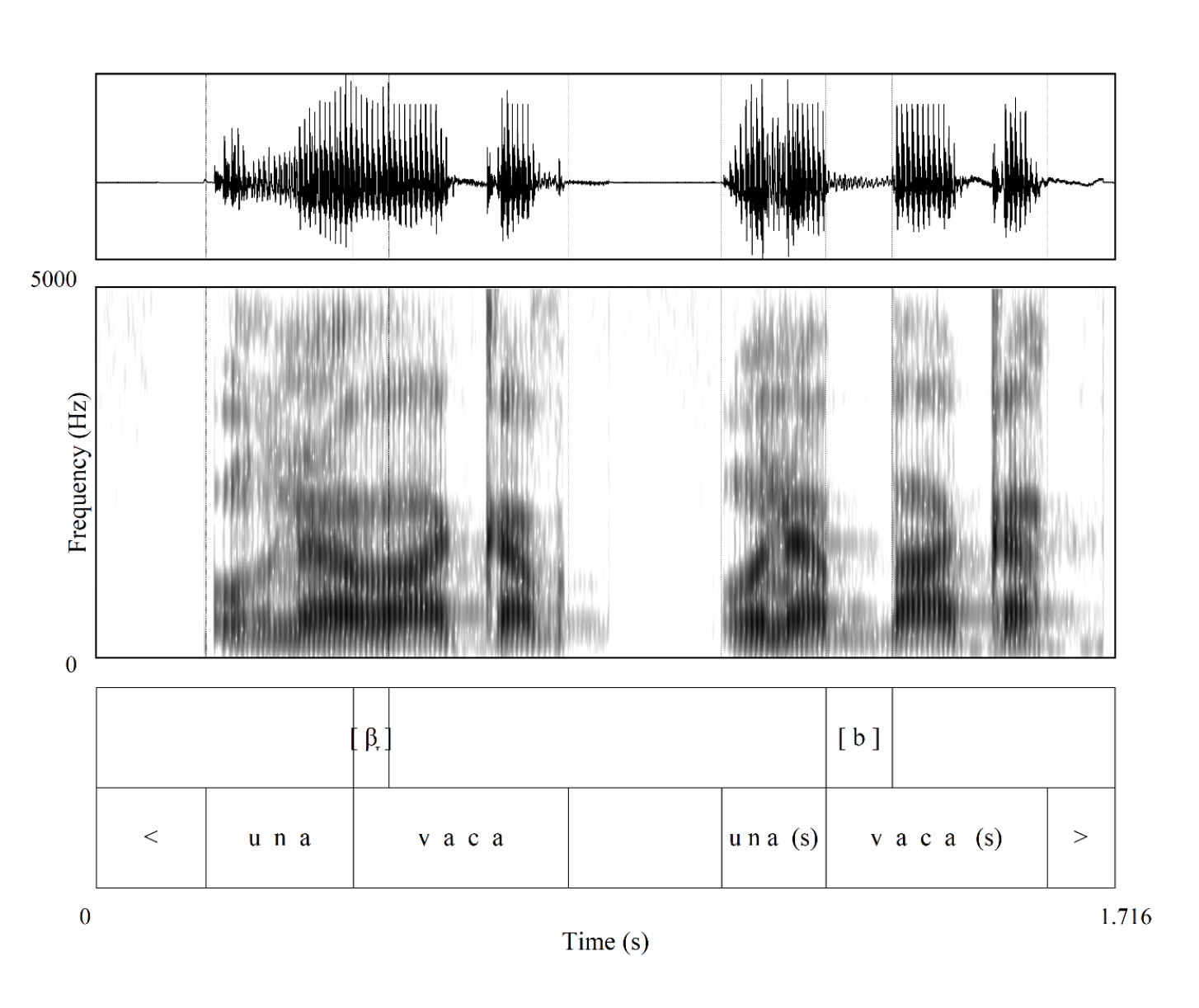
A perennial topic in the Hispanic linguistics literature is the weakening of coda /s/, explored historically, dialectally, and sociolinguistically (for a recent overview, see Núñez-Méndez (2022)). The current study examines the perception of Puerto Rican speech of deleted coda /s/ and the voiced stop series /bdg/ in minimal pair contexts, i.e., una vaca ‘a cow’ and unas vacas ‘some cows’. The singular allophones are produced as approximants [β̞ ð̞ ɣ̞] and with the /sb, sd, sd/ sequences as voiced occlusives [bdg] (see Figure 1), previously mentioned in production studies (Luna 2010, 2017; Galarza et al. 2014).
Following the methodology of Arróniz and Willis for Andalusian Spanish (2023), four Puerto Rican speech actors recorded twelve utterances with singular and plural photograph prompts of the type una vaca or unas vacas (see Figure 1 for sample spectrograms). A Qualtrics survey incorporated the audios with two question types, a heat map as a two-alternative-forced-choice (2afc) and a Visual analog slider. The utterances included a single production of each lexical item from each actor to avoid both versions from the same actor. Identical utterances with an overt coda [s] from two Mexican actors were included as a baseline for comparison. Thirty Mexican and fifty Puerto Rican speakers completed the survey. The results from both tasks indicate that despite the complete deletion of the fricative [s], the Puerto Rican listeners associated approximant productions with a singular interpretation and the voiced stops [bdg] with a plural meaning. In contrast, the Mexican listeners could not retrieve this meaning. A voiced-occlusive phone used by a particular community to compensate for a deleted coda /s/ provides evidence of language change at the phonological level.